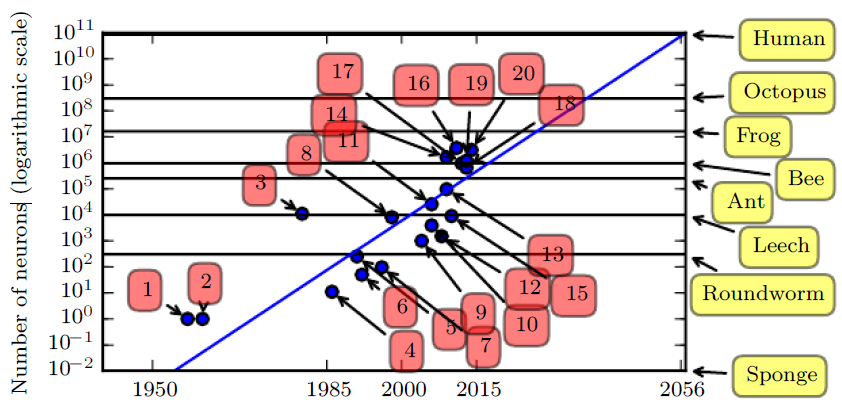
Since the introduction of hidden units, artificial neural networks have doubled in size roughly every 2.4 years.
Biological neural network sizes from Wikipedia (2015).
- Perceptron (Rosenblatt, 1958, 1962)
- Adaptive linear element (Widrow and Hoff, 1960)
- Neocognitron (Fukushima, 1980)
- Early back-propagation network (Rumelhart et al., 1986b)
- Recurrent neural network for speech recognition (Robinson and Fallside, 1991)
- Multilayer perceptron for speech recognition (Bengio et al., 1991)
- Mean field sigmoid belief network (Saul et al., 1996)
- LeNet-5 (LeCun et al., 1998b)
- Echo state network (Jaeger and Haas, 2004)
- Deep belief network (Hinton et al., 2006)
- GPU-accelerated convolutional network (Chellapilla et al., 2006)
- Deep Boltzmann machine (Salakhutdinov and Hinton, 2009a)
- GPU-accelerated deep belief network (Raina et al., 2009)
- Unsupervised convolutional network (Jarrett et al., 2009)
- GPU-accelerated multilayer perceptron (Ciresan et al., 2010)
- OMP-1 network (Coates and Ng, 2011)
- Distributed autoencoder (Le et al., 2012)
- Multi-GPU convolutional network (Krizhevsky et al., 2012)
- COTS HPC unsupervised convolutional network (Coates et al., 2013)
- GoogLeNet (Szegedy et al., 2014a)