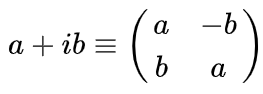The conjugate transpose or Hermitian transpose of an m-by-n matrix A with complex entries is the n-by-m matrix AH obtained from A by taking the transpose and then taking the complex conjugate of each entry.
The conjugate transpose can be motivated by noting that complex numbers can be usefully represented by 2×2 real matrices, obeying matrix addition and multiplication:
An m-by-n matrix of complex numbers could therefore equally well be represented by a 2m-by-2n matrix of real numbers.
The conjugate transpose therefore arises very naturally as the result of simply transposing such a matrix, when viewed back again as n-by-m matrix made up of complex numbers.